

Classical Music and Brain Power
Listening to classical music, such as works by Mozart, has been shown to have a positive effect on focus and concentration. Some studies ha

Talking with ChatGPT about the 777 Hz Solfeggio Frequency
777Hz Solfeggio frequency promotes positivity & clears negative thoughts for a peaceful mind. Use it in meditation, yoga or daily activities


ADHD Relief Music - increase focus/concentration/ memory - Binaural Beats
ADHD Relief Music - Increase Focus / Concentration / Memory - Binaural Beats - Focus Music | 14 Hz Binaural Beats Mental Focus / Clarity
What the new ChatGPT says about binaural and polyrythmic beats
What the new openAI ChatGPT says about Polyrythmic and Binaural Beats


Music | Positive Energy Binaural Beats 777Hz and the Science of Solfeggio Frequencies
777 Hz + 432 Hz Attract Positivity, Luck, Abundance: Reprogram your Mind for Success - Binaural Beats Finalized Thesis statement: Sound...


Classical Relaxation Mix | Ambient Chill Remix
Created with Logic Pro X and this tutorial:


Binaural Beats and Calming Music - What are they and how you can make them in Logic Pro X
Binaural beats (or binaural tones or binaural shift) are auditory processing artifacts, or apparent sounds, the perception of which...


ADHD Binaural Beats - Best Focus Music for Natural ADHD Relief
ADHD Relief Music - Increase Focus / Concentration / Memory - Binaural Beats - Focus Music Get your ADHD Clothing:...


ADHD Relief Music: Poly-rhythmic Focus Music for Concentration
ADHD relief music with poly-rhythmic movement. Use this focus music during studying or other daily tasks. ~


Deep Focus Music: ADHD Relief Music for Better Concentration, Study Music
Deep Focus Music: ADHD Relief Music for Better Concentration, Study Music ~ My other channels: Sub Bass Meditation Music ►...































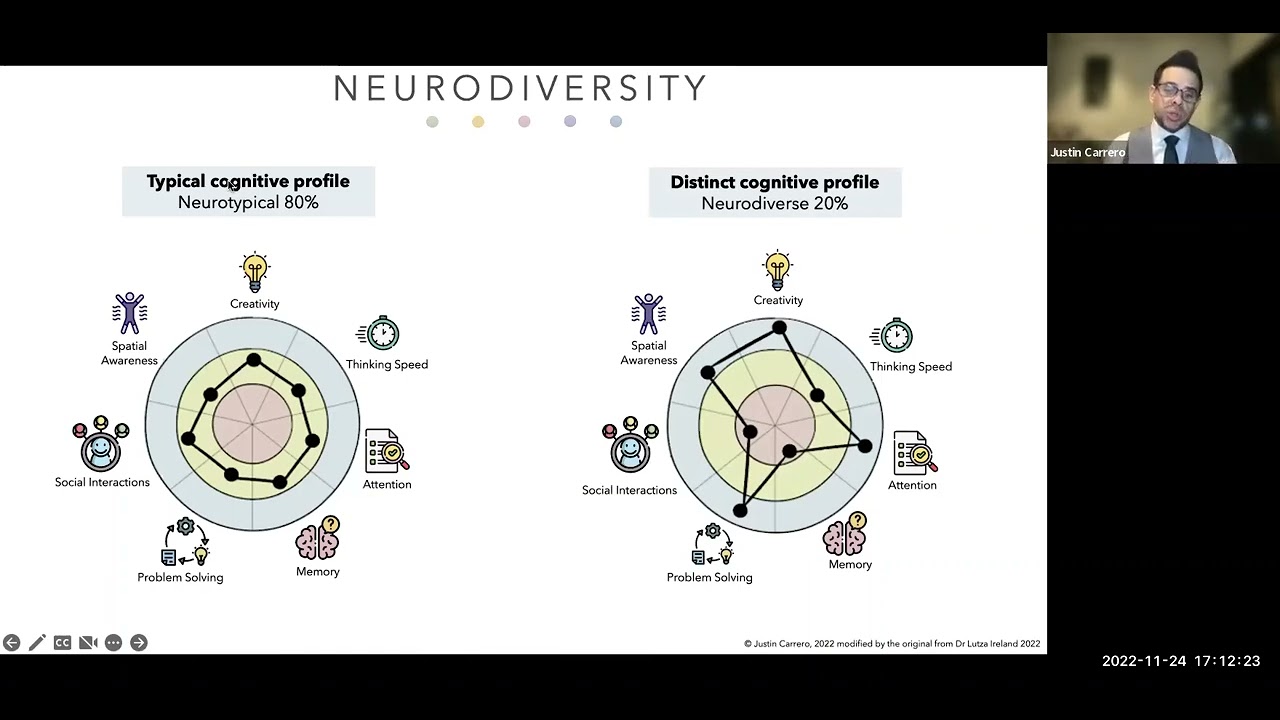


































![Neurodiversity and Leadership in the Hiring Process [draft]](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/0a19fd_a3299cad5f2041349ac65e30de6ead87~mv2.png/v1/fill/w_333,h_250,fp_0.50_0.50,q_35,blur_30,enc_avif,quality_auto/0a19fd_a3299cad5f2041349ac65e30de6ead87~mv2.webp)
![Neurodiversity and Leadership in the Hiring Process [draft]](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/0a19fd_a3299cad5f2041349ac65e30de6ead87~mv2.png/v1/fill/w_300,h_225,fp_0.50_0.50,q_95,enc_avif,quality_auto/0a19fd_a3299cad5f2041349ac65e30de6ead87~mv2.webp)



